Distributions for a Concentration-Dependent Diffusion Coefficient
Initializing live version

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
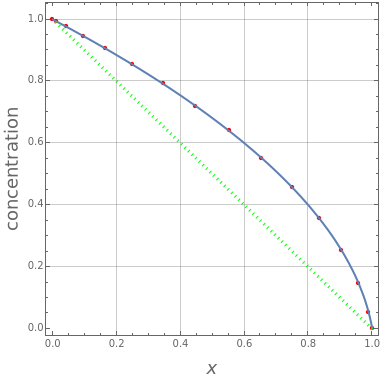
This Demonstration shows the steady-state concentration distribution through a plane sheet, a cylindrical annulus, and a spherical shell, in which diffusion is assumed to be one-dimensional. Different values of parameter  can be chosen.
can be chosen.
Contributed by: Housam Binous and Ahmed Bellagi (August 2015)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Reference
[1] J. Crank, The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed., New York: Oxford University Press, 1975.
Permanent Citation