Heat Diffusion through Different Materials

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
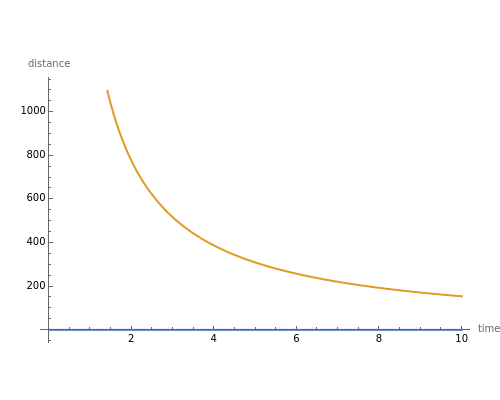
This Demonstration shows the relationship between the temperatures of materials with different thermal conductivity  at different distances along the length of the sample as a function of time when exposed to a source of heat (a small flame at 800 degrees Celsius). The
at different distances along the length of the sample as a function of time when exposed to a source of heat (a small flame at 800 degrees Celsius). The  axis is the distance in meters. As distance increases, the temperature decreases, as it is further from the flame. The
axis is the distance in meters. As distance increases, the temperature decreases, as it is further from the flame. The  axis is the temperature of the material at the specified distance on the
axis is the temperature of the material at the specified distance on the  axis. The third slider is the melting point, which determines the distance from the flame at which the material melts, as shown by the horizontal line.
axis. The third slider is the melting point, which determines the distance from the flame at which the material melts, as shown by the horizontal line.
Contributed by: Kaitlin Lewallen and Minh Pham (June 2014)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Snapshot 1: material with a low melting point  and a low thermal conductivity
and a low thermal conductivity  with a very short time; the material melts quickly and at a very low temperature
with a very short time; the material melts quickly and at a very low temperature
Snapshot 2: material with a higher  value and higher melting point, and it has been exposed to the heat for a longer period of time; the material will require a higher temperature to melt, but will melt much more of the material because of the extended exposure and still relatively low
value and higher melting point, and it has been exposed to the heat for a longer period of time; the material will require a higher temperature to melt, but will melt much more of the material because of the extended exposure and still relatively low  value
value
Snapshot 3: material with a very high melting point and a high  value, and it has been exposed to the heat for a longer period of time; not as much of the material will melt, despite the longer exposure, and it requires a higher temperature to even get the material heated up farther from the source
value, and it has been exposed to the heat for a longer period of time; not as much of the material will melt, despite the longer exposure, and it requires a higher temperature to even get the material heated up farther from the source
This Demonstration was written in Making Math.
References
[1] D. Madrzykowski. "Fire Dynamics." (Nov 17, 2010) www.nist.gov/fire/fire_behavior.cfm.
[2] TutorVista. "Heat Transfer Formula." (May 28, 2014) formulas.tutorvista.com/physics/heat-transfer-formula.html.
Permanent Citation