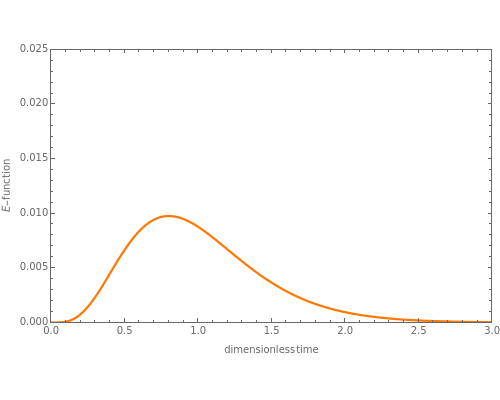
Residence Time Distribution Function of a Stirred-Tank Cascade (E-Curve)

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
A first-order isothermal reaction ( product ) is carried out in a stirred-tank reactor cascade. The
product ) is carried out in a stirred-tank reactor cascade. The  -curve is determined from a pulse input by setting the reaction rate constant equal to zero. The
-curve is determined from a pulse input by setting the reaction rate constant equal to zero. The  -curve is usually determined experimentally. It is a measure of exit-normalized concentration versus time for a tracer impulse input. We plot the steady-state concentration versus tank number using the
-curve is usually determined experimentally. It is a measure of exit-normalized concentration versus time for a tracer impulse input. We plot the steady-state concentration versus tank number using the  -curve and a first-order reaction rate constant
-curve and a first-order reaction rate constant  equal to 0.05. Of course, one can solve the governing equations (a system of ODEs) when the reaction is taking place and get the steady state concentrations of species A. Here the
equal to 0.05. Of course, one can solve the governing equations (a system of ODEs) when the reaction is taking place and get the steady state concentrations of species A. Here the  -curve is used instead.
-curve is used instead.
Contributed by: Housam Binous (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
The  -curve is obtained by using
-curve is obtained by using  .
.
The steady-state concentration is obtained using the  -curve and this relationship:
-curve and this relationship:
 .
.
Permanent Citation