Simplified Statistical Model for Equilibrium Constant

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
Consider a simple chemical equilibrium  with equilibrium constant
with equilibrium constant  . (This can alternatively be written
. (This can alternatively be written  in terms of the concentrations of
in terms of the concentrations of  and
and  .) The difference in electronic energy for the reaction
.) The difference in electronic energy for the reaction  equals
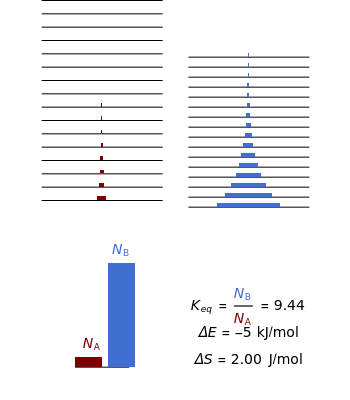
equals  , conveniently expressed in kJ/mol. Let the internal structure of each molecule be idealized as a series of equally spaced energy levels (similar to those of a harmonic oscillator), with the energy increments
, conveniently expressed in kJ/mol. Let the internal structure of each molecule be idealized as a series of equally spaced energy levels (similar to those of a harmonic oscillator), with the energy increments  and
and  . The spacings
. The spacings  and
and  relative to
relative to  are exaggerated in the graphic for easier visualization. The sublevels of each molecular species are assumed to occupy a Boltzmann distribution at temperature
are exaggerated in the graphic for easier visualization. The sublevels of each molecular species are assumed to occupy a Boltzmann distribution at temperature  . Accordingly,
. Accordingly,  , where
, where  , the molecular partition function for
, the molecular partition function for  , and analogously for
, and analogously for  . For a mixture of
. For a mixture of  and
and  , a single Boltzmann distribution can be considered to apply for the composite levels of both molecules. This leads to the formula for equilibrium constant in statistical thermodynamics:
, a single Boltzmann distribution can be considered to apply for the composite levels of both molecules. This leads to the formula for equilibrium constant in statistical thermodynamics:  .
.
Contributed by: S. M. Blinder (March 2011)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Snapshot 1: a strongly exothermic forward reaction
Snapshot 2: an endothermic forward reaction enabled by entropy effect
Snapshot 3: effect of higher temperature
Reference
[1] D. A. McQuarrie, Statistical Mechanics, New York: Harper & Row, 1976 pp. 142 ff.
Permanent Citation