Flash Distillation of a Mixture of Four Hydrocarbons

Requires a Wolfram Notebook System
Interact on desktop, mobile and cloud with the free Wolfram Player or other Wolfram Language products.
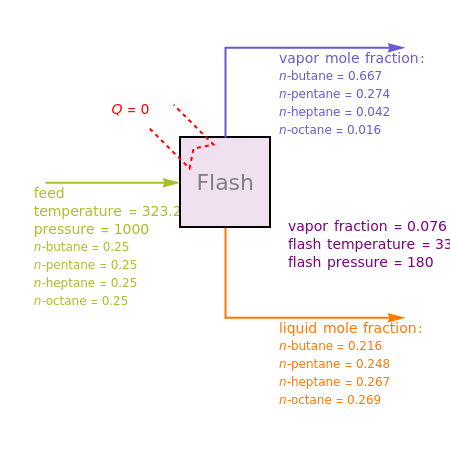
Consider a liquid feed composed of  ‐butane,
‐butane,  ‐pentane,
‐pentane,  ‐heptane, and
‐heptane, and  ‐octane at 50 °C and 1000 kPa. The feed has a flow rate of 10 kmol/hr and contains
‐octane at 50 °C and 1000 kPa. The feed has a flow rate of 10 kmol/hr and contains  mole% for each of the four hydrocarbons.
mole% for each of the four hydrocarbons.
Contributed by: Housam Binous, Naim Faqir, and Brian G. Higgins (November 2012)
Open content licensed under CC BY-NC-SA
Snapshots
Details
Fugacity coefficients as well as enthalpy correction functions are calculated using the Peng–Robinson equation of state [1, 2].
Expressions for ideal-gas constant-pressure heat capacities were obtained from Aspen-HYSYS.
References
[1] E. J. Henley and J. D. Seader, Equilibrium-Stage Separation Operations in Chemical Engineering, New York: Wiley, 1981.
[2] D-Y. Peng and D. B. Robinson, "A New Two-Constant Equation of State," Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Fundamentals, 15(1), 1976 pp. 59–64. DOI: 10.1021/i160057a011
Permanent Citation